In order to preserve their culinary secrets, chefs need to be careful with who has access to their recipes and ingredients. Export controls follow the same logic in order to ensure national stability and safeguard the interests of private companies and the State. The state regulates who can export and receive sensitive goods and technologies through a well-defined regulatory framework.
The importance of protecting your ingredients and respecting the recipe
You might be surprised about how dangerous certain ingredients can become in the wrong hands!
Let’s take the example of a company that manufactures surveillance technology. If these cameras and drones can be used to monitor sensitive areas or for military operations, it is imperative to control who can buy them. Just as a chef protects his culinary secrets, governments have introduced export controls to preserve national know-how and control its distribution around the world.
The recipe for successful export controls
Each country establishes a set of rules to determine which products, technologies and information can be sent to which recipients. Export control is, in a way, a recipe book with instructions designed to ensure that each ‘ingredient’ cannot fall into the hands of another ill-intentioned chef. It is a tool for preventing and guaranteeing national and international security.
Which ingredients are subject to export controls?
The products subject to these controls are listed in the regulations of each country. There are two types of categories: dual-use goods (products that can be used for both civilian and military purposes) and military goods. Military goods include, for example, weapons and cutting-edge technology, but dual-use goods also include certain chemical products. Sometimes, certain types of goods can be found in both lists (e.g. aeronautics & chemicals). However, their different functionalities, design and use determine whether they are classified as military goods or dual-use goods.
Export controls are not limited to listed goods. In fact, controls can be applied to goods that are not specifically mentioned in the regulations, but they still may be considered sensitive depending on their use. This principle makes it possible to control goods whose implications are not obvious and to prevent inappropriate use. For example, there are chemicals intended for legitimate applications that can be used to manufacture weapons. The aim here is also to prevent the diversion of products. Here, for example, the cook can use eggs in many different recipes!
Who manages the kitchen?
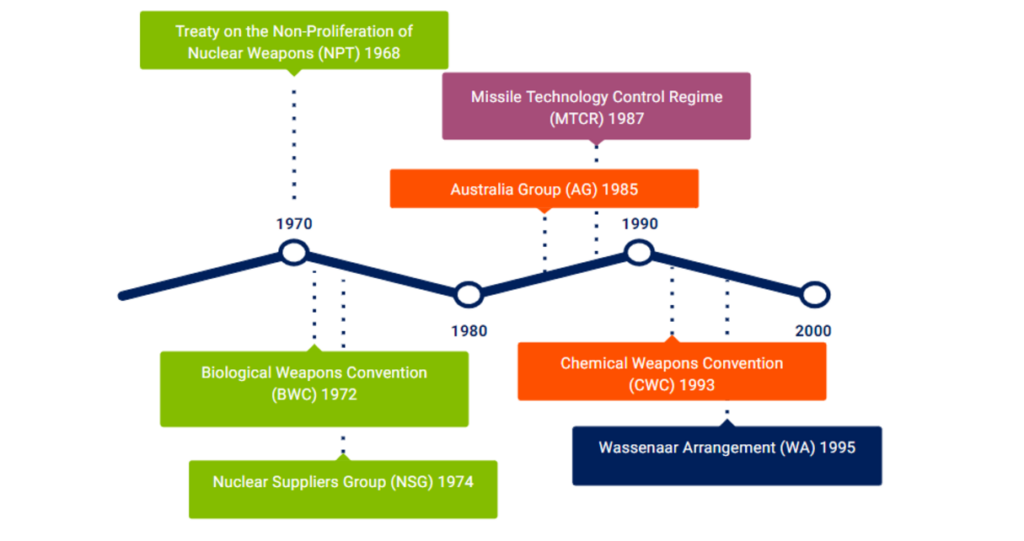
Export controls are governed by various international treaties, agreements and regulations. Each country has its own rules, just as each chef has their own style of cooking. To prevent secret recipes from spreading where they shouldn’t, several authorities are involved in the kitchen:
- In the United States, the DDTC (Directorate of Defense Trade Controls – Department of State), the BIS (Bureau of Industry and Security – Department of Commerce) and the OFAC (Office of Foreign Assets Control – Department of Treasury) supervise everything and make sure that the rules are followed.
- In France, we have the SBDU (Service des Biens à Double Usage), the DGA (Direction Genérale de l‘Armement) and, in some cases, the ANSSI (National Cybersecurity Agency of France).
As a result, every company must adapt to existing regulatory frameworks and ensure that regulations are properly applied by demonstrating compliance.
To ensure the expected compliance, it is necessary to look at several elements, which will enable the compliance elements to be verified, rather like when a cook is checking the quality of the ingredients used. With regard to export controls, it is important to know how to answer four fundamental questions:
- Who is involved in the operation?
- What are we talking about in terms of operations?
- Where is the operation located?
- What is the purpose of the operation?
Once these answers have been obtained, the compliance actions will vary, with different levels of constraints. Indeed, the application of regulations will vary, with their share of national, European and international specificities. For example, the origin of the goods and their destination will be two decisive criteria in the regulations to be applied.
It’s important to bear in mind that several regulations can apply simultaneously!
What are the risks of making a mistake?
The failure to classify products correctly, the management of intangibles and the evaluation of stakeholders are three problems often encountered by different entities. Our experts are here to help you identify good practice, particularly in this context, so that you don’t make mistakes that could cost your business dearly!
In fact, export controls often have a limited reputation compared with the real impact of these regulations, which do not only concern ‘pure and simple’ exports, but are involved in all stages of the supply chain.
As a reminder, a chef who does not comply with hygiene rules risks having his kitchen closed. In export control, it’s the same thing. When a company ignores the regulations, it risks civil, criminal and administrative penalties (substantial fines, imprisonment, loss of export authorisations, etc.).
Conclusion: don’t underestimate export controls!
Export controls, like cooking, highlight the art of protecting what is precious, while at the same time enable beneficial exchanges, whether for entities or gourmet customers. To do this, you need to follow the recipe without skipping any steps.
The next time someone talks to you about export controls, think of the chef who wants to protect his secrets while sharing his talent. You’ll never look at a recipe in the same way again, will you!
Advice from our experts
- Make sure you have good internal communication with your teams and other departments. This will help you avoid export control failures!
- Raise awareness, have a clear procedure and carry out internal audits.
- If you feel uncomfortable, seek help! Discover Airbus Protect’s services.
Every situation is different and there are multiple ways of doing things, so you shouldn’t hesitate to take the plunge into a restaurant… or into compliance.
 Cybersecurity
Cybersecurity 





